
How the bimetal provides thermal regulation without energy?
In brief!
Bimetal technology enables mechanical action based on temperature without any electrical power supply, by exploiting the physical properties of two metals with different thermal expansion coefficients. Used for decades in the electrical component industry, this passive and autonomous solution is now more relevant than ever to meet the growing demand for thermal regulation in constrained environments (HVAC systems, fire safety, protection of sensitive components, etc.).
Reliable, accurate, and maintenance-free, bimetal technology represents a strategic alternative to electronic solutions, especially in contexts where electrical power is limited, risks are high, or simplicity is essential.
Introduction: the challenges of autonomous thermal regulation
Why choose thermal regulation without external energy input?
In many industrial environments, access to a reliable electrical power supply cannot be guaranteed. Environmental constraints, safety regulations, or design simplicity often require thermal regulation systems capable of operating fully autonomously. In such cases, passive solutions that respond directly to temperature variations without relying on sensors, control units, or external power sources offer a decisive advantage in terms of reliability and robustness.
The limitations of electronic or motorized solutions
Active thermal regulation systems rely on electrical power, electronic control, and regular maintenance. They are subject to potential failures, signal losses, or power outages. In critical sectors such as fire safety, nuclear facilities, transportation, or industrial infrastructure, absolute reliability and immediate response without electrical dependency are essential. Any failure of the control chain can compromise safety.
The bimetal solution: a passive, reliable, and durable technology
Bimetal technology provides a simple and effective response to these challenges. Its purely physical and automatic reaction to temperature variations ensures exceptional robustness and long service life, with no need for external control, electronics, or maintenance.
Understanding the bimetal principle
What is a bimetal? Structure and basic operating principle
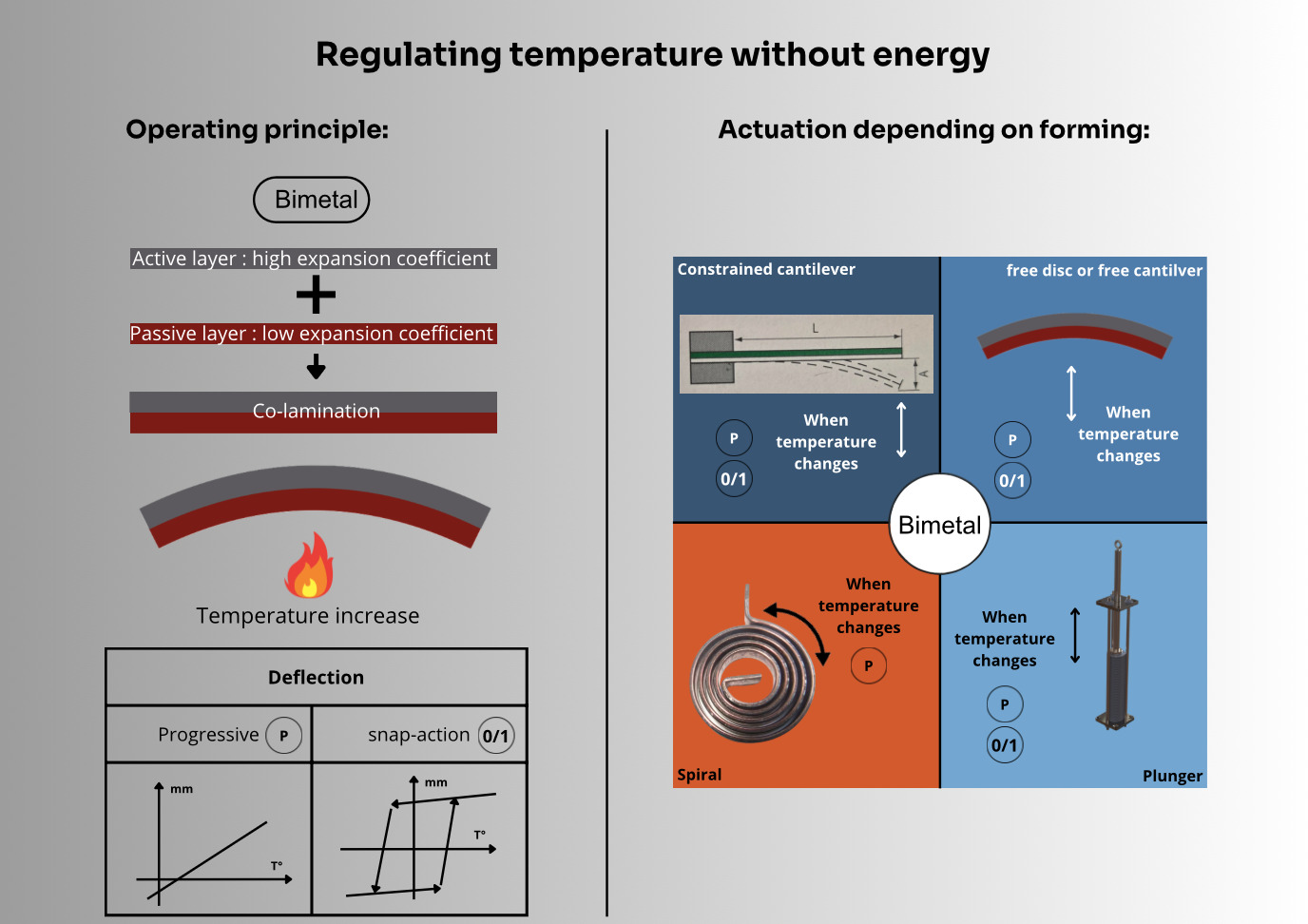
A bimetal consists of two different metal strips bonded together through industrial co-lamination. Each metal has a distinct coefficient of thermal expansion. When the temperature changes—either heating or cooling—one metal expands or contracts more than the other. This differential expansion causes the bimetal strip to bend in a predictable and repeatable manner.
Physical properties involved: differential expansion, shape memory, and thermal hysteresis
Bimetal operation relies primarily on differential thermal expansion. Over a certain temperature range, the deformation of the bimetal is generally linear and repeatable. When returning to its initial temperature, the bimetal exhibits shape memory behavior. With appropriate forming, the bimetal can also be designed to produce a snap-through effect (reversible or irreversible), known as bistable effect or hysteresis.
Types of bimetals: spiral, disc, and cantilever (flat strip)
Depending on the intended application, bimetals can take various shapes and mechanical behaviors: Spiral shape for rotational movements, disc or cantilever shape for linear movements. A disc or cantilever bimetal may be used either in linear continuous deformation mode or in abrupt snap-action mode.
Bimetal thermal actuators: applications and benefits
How a bimetal actuator works
When heated or cooled, the deformation of the bimetal is converted into mechanical movement. This movement can be used to actuate a flap, trigger a switch, or activate a safety mechanism. The actuator operates directly from temperature, without any intermediary energy conversion.
Responsiveness and accuracy: trigger curves and thermal cycles
Bimetal actuators are calibrated to respond to precise temperature variations. Their performance is defined by displacement curves or switching curves, which are essential for proper integration into a system. They are designed to withstand repeated thermal cycles while maintaining consistent triggering behavior.
Industrial advantages: no power supply, reliability, long service life, ease of integration
Their autonomy, minimal maintenance requirements, and ability to operate in harsh environments make bimetal actuators highly valued components in demanding industrial applications.
Concrete industrial use cases
Fire dampers and thermal locks for passive fire safety (HVAC, construction)
Bimetals are widely used to actuate fire dampers in ventilation systems, ensuring automatic closure when excessive temperatures are detected. They are also integrated into fire door latches, enabling automatic locking or unlocking without any electrical command.
Temperature threshold indicators for cold-chain transportation
Bimetals can activate mechanical visual indicators or control electrical contacts connected to warning lights when a temperature threshold is exceeded—whether for cold (freezing risk) or heat (overheating).
Protection against battery or electrical enclosure overheating
Bimetal components can switch off a circuit, actuate a mechanical or electrical command, or trigger an alarm when temperature exceeds a critical limit—without requiring external power.
Contact thermostats for ventilation ducts
Mounted directly on air ducts, these thermostats use bimetal elements to measure and react to airflow temperature by autonomously controlling an electrical contact.
Resettable thermal circuit breakers: operating principle
Thermal circuit breakers use bimetal heating via the Joule effect (current-induced heating). When the current exceeds a predefined limit, the bimetal reaches a critical temperature and opens the circuit. Once cooled, the breaker can be reset manually or automatically.
Autonomous regulation in embedded or isolated systems (buildings, vehicles, passive IoT)
In environments where power supply is intermittent or absent, bimetal technology provides a reliable solution to maintain thermal control functions.
Choosing the right bimetal mechanism for your application
Thermal sensor, actuator, or circuit breaker: what are the differences?
A thermal sensor provides information, an actuator performs a mechanical action, and a circuit breaker interrupts an electrical circuit. The appropriate choice depends on the function required within the system. Understanding this distinction is essential to selecting the correct bimetal-based solution for a given application.
Selection criteria: operating or triggering temperatures, mechanical force, size constraints
Each application requires a specific configuration. Manufacturers offer calibrated solutions adapted to precise technical requirements.
Custom solutions: why work with a specialized manufacturer?
Only an experienced manufacturer can guarantee a customized mechanical movement adapted to the thermal environment, while ensuring repeatability, compliance with applicable standards, and full integration into the final operating conditions.
Integration, standards, and future perspectives
Applicable technical standards (EN, ISO, UL, etc.)
Devices incorporating bimetal components must comply with strict safety and quality standards, depending on their field of application.
Integration considerations in product design
Form factor, overall dimensions, mounting points, and thermal behavior must be anticipated during the design phase of the final product.
Future developments: smart materials, miniaturization, hybrid solutions
Future bimetal technologies may offer increased accuracy, reduced size, faster response times, or hybrid integration with electronic sensors in combined solutions.
Infographic: bimetal operation at a glance
A simple mechanism to understand… yet highly strategic
Because a diagram is often more effective than a long explanation, this infographic provides a visual summary of how bimetal technology works, its different formats, and its main industrial applications. It highlights the key stages of autonomous thermal regulation using bimetal elements and emphasizes the major advantages of this technology: simplicity, reliability, responsiveness, and energy independence.
Whether you are an engineer, technician, or decision-maker, this visual aid will help you better understand how to integrate a bimetal actuator into your systems or explain its operation to your teams or partners.
Enhancing your project with high-performance bimetal solutions
To meet your needs for autonomous, energy-free thermal regulation, DELTA CONCEPT offers thermosensitive components and subassemblies tailored to industrial constraints, whether standard solutions or fully customized developments.
Explore proven products for your applications:
- Thermal plungers: bimetal mechanical actuator with progressive or snap-action triggering for controlling dampers, valves, or thermal regulation systems.
- Resettable thermal fuse: thermal safety device with automatic electrical cut-off in case of overheating and reset capability without replacement.
- Standard bimetal products: a range of calibrated components offering short lead times and reliable industrial quality.
- Custom developments: design of tailored bimetal assemblies based on your technical specifications and integration requirements
Our engineering department can support you in sizing, testing, and integrating these solutions into your project. Contact our experts today for a personalized study or request a technical quotation adapted to your specifications.
FAQ: what industrial users want to know
What is the average life of a bimetal actuator?
Several decades lifetime, and up to several hundred thousand cycles, depending on the application.
Can a bimetal be adjusted or calibrated after manufacturing?
No. Calibration is performed at the factory. The correct model must be selected according to the application requirements.
Can a bimetal operate in ATEX environments or high humidity conditions?
ATEX: Yes, provided that appropriate design and encapsulation are used. Humidity: bimetals have properties similar to stainless steel, with standard precautions in saline or chemically aggressive environments.
What tolerances apply to triggering temperature?
Typically ±3 °C to ±5 °C for standard products; tighter tolerances are available on request
What is the difference between European (French) and Asian bimetals?
Mainly thermal stability, accuracy, repeatability, and compliance with European standards
Conclusion: mastering thermal control without electronics — a low-tech industrial innovation lever
In the face of energy efficiency challenges, passive safety requirements, and reliability constraints, bimetal technology stands out as a reference solution. Its integration into modern industrial systems reflects a return to fundamentals: using the laws of physics to meet critical needs without digital dependency. A model of efficiency worth rediscovering.
